
Does Glufosinate Ammonium Harm Crops? A–Z Explanation for Safe Use
Does Glufosinate Ammonium harm crops? Learn the full answer – including its effects, safe spraying practices, and important precautions to avoid leaf burn, root damage, or plant death.
Table of Contents
- What Is Glufosinate Ammonium?
- Mode of Action – Why It Can Be Harmful if Misused
- Common Cases Where Crops Are Affected
- Factors That Increase the Risk of Crop Damage
- How to Spray Glufosinate Safely
- Should Glufosinate Be Used in Orchards and Vegetable Gardens?
- Conclusion
1. What Is Glufosinate Ammonium?
Glufosinate Ammonium is a non-selective, contact herbicide that kills weeds at the point of contact.
Key Features:
- Not systemic – does not move into plant roots
- Breaks down quickly in soil
- Fast-acting and safe when used properly
👉 However, incorrect spraying can harm crops, especially young or tender parts such as new leaves and shoots.
2. Mode of Action – Why It Can Harm If Sprayed Incorrectly
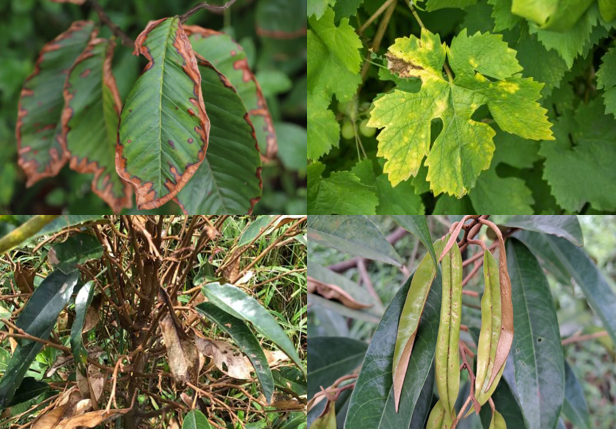

Glufosinate inhibits glutamine synthetase, leading to toxic ammonia buildup in plant cells.
When sprayed directly onto crop tissues like young leaves or shoots, symptoms may include:
- Leaf scorch or necrosis
- Yellowing of the canopy
- Shoot dieback or premature leaf drop
❗️ Particularly risky for crops like durian, mango, jackfruit, pepper, and coffee when sprayed during flush or new leaf growth.
3. Real-World Crop Damage Cases
|
Situation |
Typical Consequences |
|
Spraying against the wind |
Herbicide drifts onto canopy → leaf burn |
|
Overdosing (2–3x recommended) |
Severe yellowing, growth shock |
|
Active flush (new leaves) |
Leaf tip burn, shoot drop |
|
Spraying in intense sunlight |
Rapid evaporation → stronger reaction |
|
Poor nozzle control |
Spray hits stems/base → root collar burn |
4. Factors That Increase the Risk of Damage

- Excessive concentration (improper dilution)
- High spray pressure → wide, uncontrolled coverage
- No base protection for young trees
- Spraying during hot weather (>33°C)
- Using on recently transplanted or stressed plants
5. How to Spray Glufosinate Safely
✅ Spray close to the ground, avoid contact with stems or leaves
✅ Use flat fan nozzles, low-pressure settings for precision
✅ Shield plant bases with cardboard or mulch if young
✅ Avoid spraying during windy, rainy, or hot weather
✅ Correct dosage: 40–60ml per 16 liters of water (follow label instructions)
✅ Do not mix with alkaline substances (e.g., lime, sulfur)
6. Should Glufosinate Be Used in Orchards and Vegetable Fields?

✅ YES – if used correctly:
- Popular in durian, mango, jackfruit, coffee, rubber plantations
- Ideal for weed control around tree bases and garden paths
- Safer than Glyphosate as it does not translocate to roots
📌 Caution: Avoid spraying during flush or flowering periods
7. Conclusion
Glufosinate Ammonium does not harm crops when used properly – with the right technique, timing, and dosage.
👉 It’s a fast-acting, non-systemic herbicide well-suited for fruit orchards and clean farming systems.
However, misuse can cause serious damage like leaf burn and growth suppression, so follow safety guidelines strictly.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



